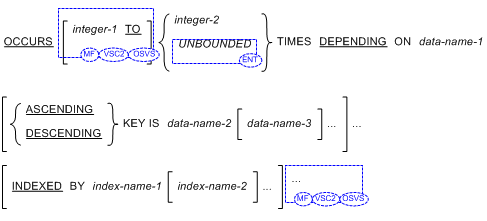
The OCCURS Clause
General Formats for Format 1

General Formats for Format 2
General Formats for Format 3
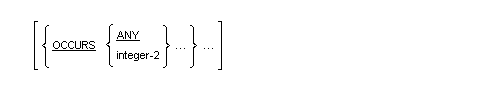
Directives
- In addition to Compiler directives which provide flagging and modify the reserved word list, the following directives may
impact either the syntax or the semantics described in this section.
- ODOOSVS – requests OS/VS COBOL compatible processing of the OCCURS DEPENDING ON clause.
- ODOSLIDE – controls the processing of nested OCCURS DEPENDING ON clauses and fixed data following an OCCURS DEPENDING ON clause.
- REENTRANT – allows a program to be used in a multi-threaded environment.
Syntax Rules
- Where both integer-1 and integer-2 are used, integer-1 must be greater than

 or equal to
or equal to
zero and integer-2 must be greater than

 or equal to
or equal to
integer-1.

 In Format 2, if "integer-1 TO" is omitted, the default value one is assumed.
In Format 2, if "integer-1 TO" is omitted, the default value one is assumed.
- The data description of data-name-1 must describe an integer.
- Data-name-1, data-name-2, data-name-3, ... can be qualified.
- Data-name-2 must be either the name of the entry containing the OCCURS clause or the name of an entry subordinate to the entry
containing the OCCURS clause.
 This restriction is removed.
This restriction is removed.
- Data-name-3, and so on, must be the name of an entry subordinate to the group item which is the subject of this entry.
 This restriction is removed.
This restriction is removed.
- An INDEXED BY phrase is required if the subject of this entry, or an entry subordinate to this entry, is to be referred to
by indexing,

 unless it is to be indexed by an index defined for another table (see the section
Indexing in the chapter
Concepts of the COBOL Language)
unless it is to be indexed by an index defined for another table (see the section
Indexing in the chapter
Concepts of the COBOL Language)
.
The index-name identified by this clause is not defined elsewhere, and not being data, cannot be associated with any data hierarchy.
- A data description entry that contains Format 2 of the OCCURS clause should only be followed, within that record description,
by data description entries which are subordinate to it.

 A data description entry that contains Format 2 of the OCCURS clause can be followed, within that record description, by data
description entries which are not subordinate to it. When the value of the data item referenced by data-name-1 is changed,
the position of data items following, but not subordinate to, the table is changed. The data these items contain can be lost.
A data description entry that contains Format 2 of the OCCURS clause can be followed, within that record description, by data
description entries which are not subordinate to it. When the value of the data item referenced by data-name-1 is changed,
the position of data items following, but not subordinate to, the table is changed. The data these items contain can be lost.
 If the NOODOSLIDE Compiler directive is set, all group items containing the table are considered as always having the maximum
number of occurrences, irrespective of the value of data-name-1 and therefore the position of the data items following the
table is not changed.
If the NOODOSLIDE Compiler directive is set, all group items containing the table are considered as always having the maximum
number of occurrences, irrespective of the value of data-name-1 and therefore the position of the data items following the
table is not changed.
- The OCCURS clause cannot be specified in a data description entry that:
- Has a 66 or 88 level-number
- Describes an item whose size is variable. The size of an item is variable if the data description of any subordinate item
contains Format 2 of the OCCURS clause.

 An OCCURS clause can be specified for a data description subordinate to another item with a Format 2 OCCURS clause.
An OCCURS clause can be specified for a data description subordinate to another item with a Format 2 OCCURS clause.
- The OCCURS clause should not be specified in a data description entry at the 01 level or as a 77 level-number.
 This restriction is removed.
This restriction is removed.
- In Format 2, the data item defined by data-name-1 must not occupy a character position within the range of the first character
position defined by the data description entry containing the OCCURS clause and the last character position defined by the
record description entry containing that OCCURS clause.

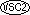 If the ODOSLIDE Compiler directive is set, data-name-1 must have a fixed location.
If the ODOSLIDE Compiler directive is set, data-name-1 must have a fixed location.
- If data-name-2 is not the subject of this entry, then:
- All of the items identified by the data-names in the KEY IS phrase must be within the group item which is the subject of this entry
- Items identified by the data-name in the KEY IS phrase must not contain an OCCURS clause
- There must not be any entry that contains an OCCURS clause between the items identified by the data-names in the KEY IS phrase and the subject of this entry.
- Index-name-1, index-name-2, ... must be unique words within the source element.
 Index-name-1, index-name-2, ... need not be unique and can be qualified by the data-name which is the subject of this entry
Index-name-1, index-name-2, ... need not be unique and can be qualified by the data-name which is the subject of this entry
.

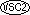
 The OCCURS clause can be specified for external or internal floating-point data items.
The OCCURS clause can be specified for external or internal floating-point data items.
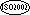 The KEY clause must not be specified for a data item of class object.
The KEY clause must not be specified for a data item of class object.

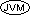 The Format 3 OCCURS clause must be specified in a data description entry at the 01 level.
The Format 3 OCCURS clause must be specified in a data description entry at the 01 level.

 If the ANY phrase is specified, it must be specified for all dimensions, whether or not OCCURS is repeated.
If the ANY phrase is specified, it must be specified for all dimensions, whether or not OCCURS is repeated.

 The subject of the entry for a Format 3 OCCURS clause must be a .NET native type as specified in the topic .NET Native Types
in the section .NET Concepts in the Language Fundamentals chapter.
The subject of the entry for a Format 3 OCCURS clause must be a .NET native type as specified in the topic .NET Native Types
in the section .NET Concepts in the Language Fundamentals chapter.
General Rules
- The OCCURS clause is used in defining tables and other homogenous sets of repeated data items. Whenever the OCCURS clause
is used, the data-name which is the subject of this entry must be either subscripted or indexed whenever it is referred to
in a statement other than SEARCH
 , SORT
, SORT
or USE FOR DEBUGGING. Further, if the subject of this entry is the name of a group item, then all data-names belonging to the group must be subscripted or indexed whenever they are used as operands, except as the object of a REDEFINES clause. (See the topics Subscripting, Indexing and Identifier in the chapter Concepts of the COBOL Language.)
- Except for the OCCURS clause itself, all data description clauses associated with an item whose description includes an OCCURS clause apply to each occurrence of the item described.
- UNBOUNDED can be used to specify an unbounded table (a table with an unbounded maximum number of occurrences), and can be referenced anywhere that a table can be referenced.
- An unbounded group is a group that contains at least one unbounded table. It can be specified only in the Linkage Section, and must be of type alphanumeric or national.
- You can reference unbounded groups in COBOL syntax anywhere that an alphanumeric or national group can be referenced, with
the following exceptions:
- You cannot specify unbounded groups as a BY CONTENT argument in a CALL statement.
- You cannot specify unbounded groups as data-name-2 on the Procedure Division RETURNING phrase.
- You cannot specify unbounded groups as arguments to intrinsic functions, except as an argument to the LENGTH intrinsic function.
- Data-name-1 must have a fixed location, and must not follow an item that contains an OCCURS DEPENDING ON clause.
- The number of occurrences of the subject entry is defined as follows:
- In Format 1, the value of integer-2 represents the exact number of occurrences.
- In Format 2, the current value of the data item referenced by data-name-1 represents the number of occurrences.
This format specifies that the subject of this entry has a variable number of occurrences. The value of integer-2 represents the maximum number of occurrences and the value of integer-1 represents the minimum number of occurrences. This does not imply that the length of the subject of the entry is variable, but that the number of occurrences is variable.
The value of the data item referenced by data-name-1 must fall within the range of integer-1 through integer-2. Reducing the value of this data item makes the contents of data items, whose occurrence numbers now exceed the value of the data item referenced by data-name-1, unpredictable.
 When a group item, having subordinate to it an entry that specifies Format 2 of the OCCURS clause, is referenced, the part
of the table area used in the operation is determined as follows:
When a group item, having subordinate to it an entry that specifies Format 2 of the OCCURS clause, is referenced, the part
of the table area used in the operation is determined as follows:
- If the data item referenced by data-name-1 is outside the group, only that part of the table area that is specified by the value of the data item referenced by data-name-1 at the start of the operation is used.
- If the data item referenced by data-name-1 is included in the same group and the group data item is referenced as a sending item, only that part of the table area that is specified by the value of the data item referenced by data-name-1 at the start of the operation is used in the operation. If the group is a receiving item, the maximum length of the group is used.
- The KEY IS phrase is used to indicate that the repeated data is arranged in ascending or descending order according to the values contained in data-name-2, data-name-3, and so on. The ascending or descending order is determined according to the rules for comparison of operands (see the topics Comparison of Numeric Operands and Comparison of Nonnumeric Operands in the topic Relation Condition in the chapter Procedure Division). The data-names are listed in their descending order of significance.
- The type of storage allocated for index-name-1, index-name-2... depends on whether or not the program is recursive (that is,
has a Local-Storage Section defined) and whether the REENTRANT Complier directive has been specified.
The first of the tables below specifies how storage is allocated for non-recursive programs. The second table specifies how storage is allocated for recursive programs.
Table 1. Storage Allocated for Index-name in Non-Recursive Program Index-name Defined in Index-name Allocated in NOREENTRANT REENTRANT (1) REENTRANT (2) working storage working storage working storage thread-local thread-local thread-local thread-local thread-local linkage working storage local storage local storage Table 2. Storage Allocated for Index-name in Recursive Program Index-name Defined in Index-name Allocated in NOREENTRANT REENTRANT (1) REENTRANT (2) working storage working storage working storage thread-local thread-local thread-local thread-local thread-local local storage local storage local storage local storage linkage local storage local storage local storage 
 An entry with a Format 3 OCCURS clause defines an array that is mapped directly to a .NET native array. In COBOL, the first
array element has the subscript one.
An entry with a Format 3 OCCURS clause defines an array that is mapped directly to a .NET native array. In COBOL, the first
array element has the subscript one.

 If the ANY phrase is specified, a SET statement with either the SIZE phrase or the CONTENT phrase must be executed on the
array before an element of the array can be referenced.
If the ANY phrase is specified, a SET statement with either the SIZE phrase or the CONTENT phrase must be executed on the
array before an element of the array can be referenced.

 A Format 3 OCCURS clause that repeats the option containing ANY and integer-2 defines a rectangular array, one in which all
rows and columns have the same size.
A Format 3 OCCURS clause that repeats the option containing ANY and integer-2 defines a rectangular array, one in which all
rows and columns have the same size.

 Repetition of the Format 3 OCCURS clause defines a jagged array, or an array of arrays in which the various sub-arrays can
have different lengths.
Repetition of the Format 3 OCCURS clause defines a jagged array, or an array of arrays in which the various sub-arrays can
have different lengths.